You might not be familiar with the name but rest assured you are also a part of the quick commerce industry. After the pandemic, the supply chain of goods was disrupted greatly which led to the emergence of the q-commerce industry. Quick commerce or q-commerce is a delivery business where your order reaches you within 10 to 20 minutes.
Told you, you are already a part of the industry. There is rarely anyone in this day and time who hasn’t availed the advantage of a 15-minute-delivery. Now let us delve deeper into this unique business model.
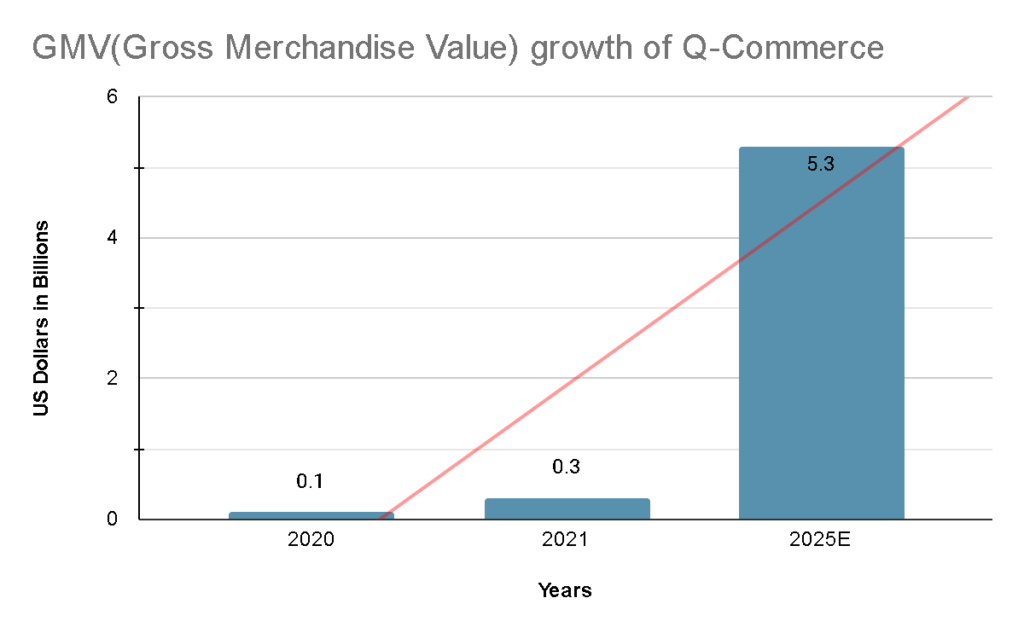
Table of Contents
Is Quick Commerce a Part of the E-Commerce Industry?
Quick commerce came into our lives when e-commerce or electronic transactions widened its scope to deliver frozen food, vegetables, fish, and groceries. The e-commerce industry is currently worth 13 trillion US dollars, thanks to quick commerce. So, technically q-commerce is a part of the e-commerce industry but with more innovative ways of achieving that last mile delivery.
The last mile delivery is the final step of delivering goods where the package is actually on the move. Quick commerce has achieved the way to deliver goods within a very limited period. This is where q-commerce is different from e-commerce.
Features of a Quick Commerce Business
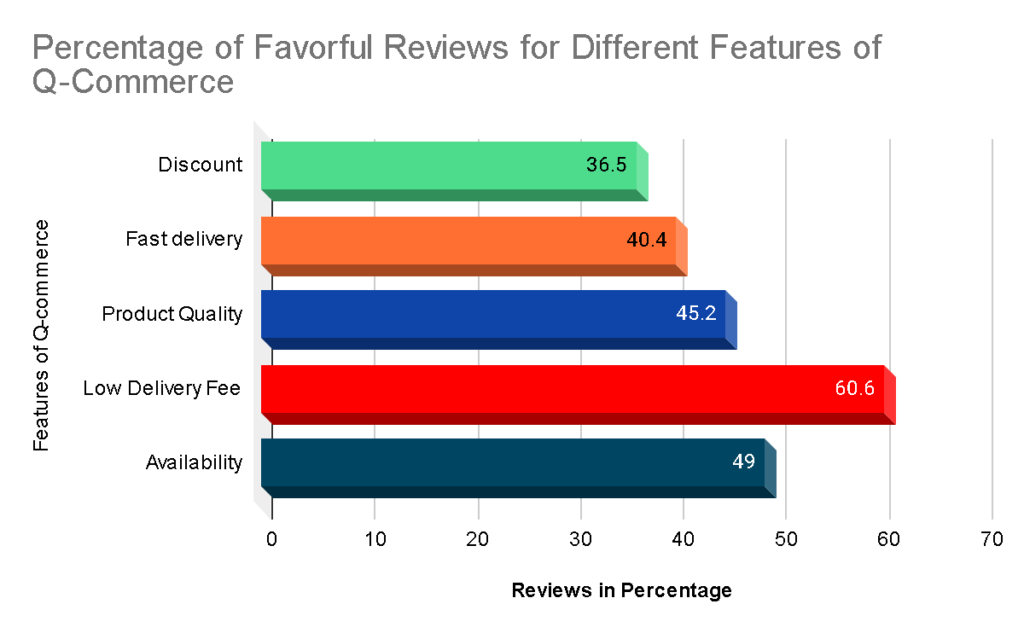
The q-commerce business has features that are very unique from the overall e-commerce industry. Let us check out why you should choose q-commerce to make your daily life a little easier.
- Faster Delivery: The primary focus of a q-commerce business is to provide you with delivery as quick as lightning. So, as an ever-busy millennial, you don’t have to waste your time by physically visiting the stores.
- Convenient: You have to admit, it is convenient to get important things delivered just by tapping on your phone in-between meetings.
- Anytime Delivery: Having multiple warehouses in important areas in metropolitan cities, and having ties with local delivery businesses has enabled the q-commerce industry to make deliveries at a time that suits the customer.
- Order-tracking: Impatient and anxious as we are, the feature of tracking the order has ensured that we always have sufficient information and remain anxiety-free.
- Shopping Apps: The q-commerce business has developed apps so that customers can order various products from one platform.
Explaining the Business Model of Quick Commerce
There are three business models that a quick commerce business can follow,
- In the Vertically integrated model, the marketplace receives orders, accumulates them, and then delivers them. The vertically integrated model uses dark grocery stores and warehouses to deliver the order after receiving the order directly from the customer. Marketplaces like Gopuff follow this business model.
- In the Delivery Platform model, which is the most popular model, customers put in the order from the online application. Dominos, the huge pizza chain, follows the delivery platform model.
- Lastly, in the Direct-to-Customer or D2C model, the aggregator uses a platform to receive the order and then uses a 3PL(third-party logistics) system to deliver them. Q commerce providers like Ohi follow the D2C model.
So, how exactly does this trillion-dollar business work, you might ask? See for yourself.
Focusing on Delivering High-Demand Items
All business models of the q-commerce industry use this strategy. As we can see, start-up q-commerce businesses cost quite a bit. So, instead of storing all kinds of amenities and groceries, the brands use a limited amount of storage space and warehouses to store the frequently ordered things. This helps reduce the cost of renting huge spaces for no good reason.
Using Micro Warehouses to Increase Efficiency
This is another technique to save money and time. Micro warehouses are like storage spaces that q-commerce businesses use to store in-demand items. These warehouses are rented in the hearts of metropolitan cities, in areas with high online presence, rent, demand, and visibility. Having these warehouses makes it easy for the delivery partners to pick up things and deliver them on time.
Planned Deliveries
Every q-commerce business divides the total delivery area into zones. Then they allocate the delivery partners on specific routes covering a small part of each zone. This is strategized in a way so that maximum deliveries can be made in the shortest period without exceeding the budget for delivery partners.
Delivery Pricing
Q-commerce businesses charge a small fee from the customers to cover the costs of setting up a brand. This fee is nominal so the customers don’t mind paying it in exchange for the convenience of the last-mile delivery.
Benefits of Quick Commerce
Competitive USP(Unique Selling Points)
Customers can have access to a rather unique mix of amenities through Q-commerce, including quick delivery, guaranteed product availability, and a wider selection than in traditional markets. The majority of Q-commerce websites also make use of technologies that track demand and alter inventory accordingly. When coupled with facilities such as any-time delivery and order-tracking, Q-commerce sites provide stiff competition to other commercial markets.
Unmatched Customer Experience
For several reasons, q-commerce provides an unrivaled customer experience. It provides a remarkably comfortable experience by fusing the benefits of conventional marketing with the ease of online shopping. One of the main arguments for choosing traditional marketing over online shopping is that the products are immediately available. With the introduction of q-commerce facilities, the consumer can save both time and effort. It can take care of any of your last-minute additions, pressing needs, and cravings!
Opportunity for Local Delivery Partners
When you are trying to get goods delivered within 15 minutes to 1 hour you need local delivery partners to be available. Even though most quick commerce businesses operate through warehouses on an aggregator business model, it gives employment opportunities to multiple delivery partners in an area. Having area-based delivery partners who actually know the city is insanely smart and convenient for the customer.
Huge Range of Products
In the online shopping apps developed by the q-commerce business, you get everything from groceries to clothes to skincare products and even electronics. With the advent of cloud kitchens and ghost kitchens, the q-commerce business has expanded even in readymade food delivery. Can you imagine any physical store in your local market offering that kind of variety? This, of course, helps build a unique sense of reliability for the customer.
Reduced Logistics Cost
Local deliveries can be cheaper than using standard shipping firms and quicker. The q-commerce sites make complete use of this fact. Stores also don’t have to give up valuable square footage to accommodate customers browsing aisles because every inch of their floor plan has been streamlined for efficiency. When orders are prepared, couriers can quickly travel between stores and clients’ locations. This results in less money spent on logistics for these deliveries and more funds available.
Great Customer Acquisition Strategy
By offering a low-cost last-mile delivery solution, Q-commerce has developed a new kind of market. Due to the ability to provide customers greater convenience than their competitors while charging less, businesses are now able to compete not only with online stores but also with local markets. Q-commerce presents a chance for market expansion by establishing cloud stores in several cities or nations.
Such businesses may eventually broaden their business models to include a variety of other services in addition to the delivery of a restricted number of goods. Due to their ability to outsource delivery operations and grow their own business at the same time, startups can accomplish this level of growth considerably more quickly than more established e-commerce enterprises.
Examples of Quick Commerce Companies
Gorillas
Gorillas is a German on-demand delivery store. They use dark stores as a business model and employ the vertically integrated technique to deliver orders within 10 to 20 minutes. It has over 200 micro warehouses in over 50 cities across seven countries.
Delivery Hero
Delivery Hero is also an on-demand food delivery store based in Berlin, Germany. They have ties with over 500,000 restaurants worldwide in 50 countries in Asia, Latin America, Europe, and the Middle East. Although it started out as solely a food-delivery business, now it has expanded and become one of the leading brands in the quick commerce industry.
BlinkIt
BlinkIt is an instant-delivery service founded in 2013. It is a perfect example of what all q-commerce brands are trying to achieve. BlinkIt delivers a range of products starting from household goods to clothes and groceries. BlinkIt is based in Gurgaon, India.
Gopuff
Gopuff is a USA-based quick commerce brand founded in 2013. It now operates in 650 cities in the US and also in Newcastle, Europe. They have over 500 micro warehouses to fulfill deliveries in the cities that Gopuff operates in. They are headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania in the US.
Instacart
Instacart is different from the rest of the companies listed here. They are not only an instant delivery business but also a pick-up service. Instacart is an American company, currently operating in the USA and Canada. The software of Instacart allows the customer’s shopping to be done by a personal shopper from the retailers involved.
The q-commerce industry relies on strategic delivery systems, local delivery partners, and micro warehouses based in
The q-commerce businesses charge a little fee for the deliveries to cover the high-cost setup for that last mile delivery and offer a huge range of products to retain a reliable customer base. There are also delivery subscription models like Zomato pro and Swiggy one.
A dark grocery store or a dark shopping mall exists solely for the purpose of online delivery in different areas from where the delivery partners pick up their orders.

